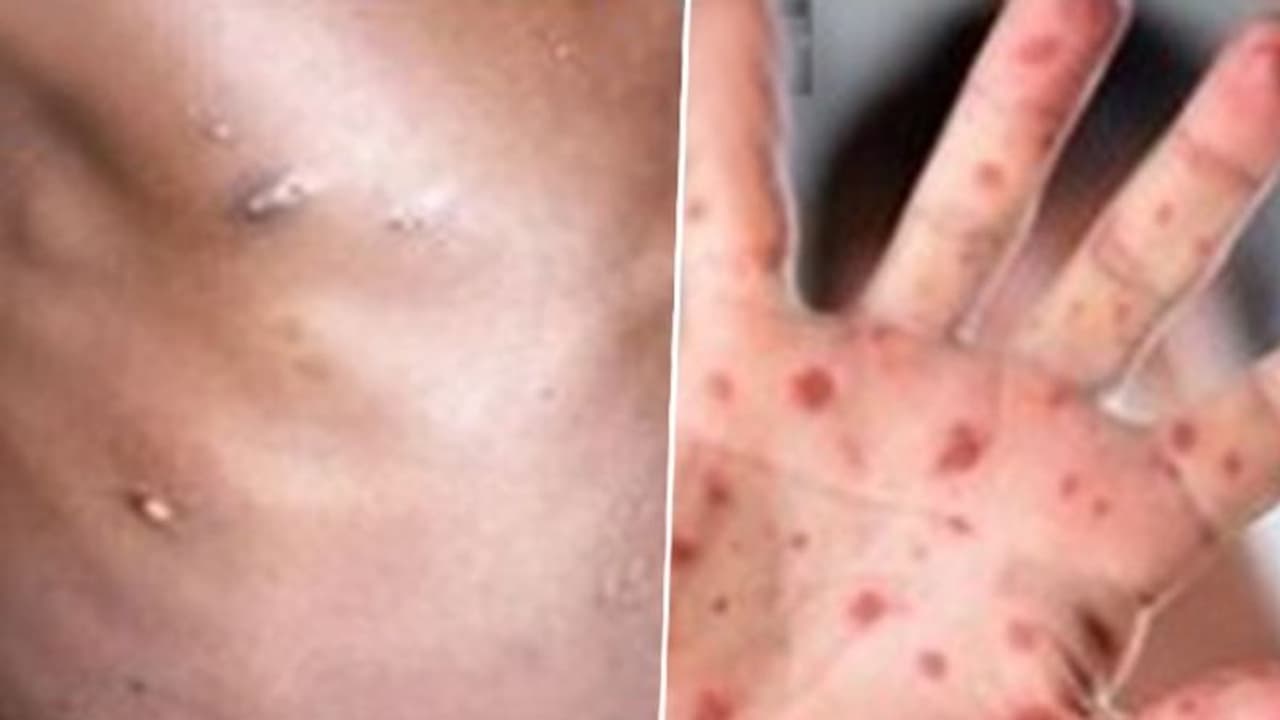
The disease is known as tomato flu due to its main symptom, red blisters that resemble tomatoes when enlarged. Fever, fatigue, body aches, skin rashes, severe joint pain, and dehydration are all symptoms of tomato flu.
The Health Ministry has issued recommendations to states and union territories regarding hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), famously known as Tomato Flu. Although tomato flu is a viral infection, it is not linked to other viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, Monkeypox, dengue, and/or chikungunya, as per the advisory.

The ministry advisory added that tomato flu, or HFMD, is a self-limiting disease with no specific treatment. According to the advisory, the illness will be best classified as a clinical variant of the viral hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common infectious disease that primarily affects young children between the ages of 1 and 10 and immune-compromised adults, as well as occasionally exposed immune component adults.
About Tomato flu
The disease is called tomato flu due to its main symptom, red blisters resembling tomatoes when enlarged. Tomato flu symptoms include fever, fatigue, body aches, skin rashes, severe joint pain, and dehydration. Other symptoms include nausea, diarrhoea, dehydration, and common influenza-like symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment for tomato flu is similar to that for other viral infections. It consists of isolation, rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and using a hot water sponge to relieve irritation and rashes. To avoid infection, the patient should be isolated for 5-7 days after the onset of any symptoms. The health ministry recommended "supportive paracetamol therapy for fever, body discomfort, and other symptomatic therapies."
Precautions
Good hygiene and sanitation of surrounding necessities and the environment are important for tomato flu prevention. It is recommended that infected children should not share food, clothing, toys, or other items with non-infected children.
About Monkeypox
Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis or virus transmitted to humans through animals and causes symptoms similar to smallpox but less severe. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines key monkeypox symptoms as fever, rashes, and swollen lymph nodes. In some cases, this can result in several medical complications.
Tomato Flu vs Monkeypox
No specific drug or vaccine exists to treat HFMD or tomato flu; newer vaccines have been developed, one of which is even approved for the treatment of Monkeypox. According to the WHO, an antiviral agent developed initially for smallpox has been approved for the treatment of Monkeypox. Tomato flu is only found in children.
Contacts with Monkeypox must be monitored at least daily for any symptoms or signs of the disease for 21 days after the last contact with a patient or contaminated material during the infection. In the case of tomato flu or HFMD, however, 5-7 days of isolation is sufficient.
If a fever is reported, a lab test is necessary to confirm or rule out disease in monkeypox and tomato flu.
Also Read: Tomato flu: Centre's new advisory says maintain proper hygiene, use warm water & more
Also Read: Tomato flu spreading in India; What are symptoms? Know treatment, precautionary steps
Also Read: Delhi reports 4th monkeypox case as Nigerian woman tests positive; takes India's tally to 9